Editorial Reviews. Review. "This volume is well written and illustrated. It will provide a useful Pesticides In Agriculture And The Environment (Books in Soils , Plants, and the Environment) - Kindle edition by WILLIS B. WHEELER, Willis B.
Table of contents
- Looking for other ways to read this?
- Sources of Agricultural Pesticides
- Agricultural Pesticides and Human Health
Warmer temperatures tend to accelerate physical, chemical, and biological processes such as volatility, water solubility, and microbial degradation, respectively. High winds and high evaporation rates may accelerate volatilization and other processes that contribute to gaseous losses of pesticides.
Management practices such as the rate and timing of pesticide applications and the mode of pesticide application also affect pesticide transport processes. The recommended practices Porter and Stimman, ; U.
Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, include pesticide use only when and where it is necessary and in amounts adequate to control pests. Those who use pesticides should carefully follow the directions on the label to minimize harmful effects to the applicator as well as potential losses to the environment. Pesticide users should select pesticides that are less likely to leach. Irrigation should be avoided shortly after pesticide application, to reduce losses through runoff and leaching. The best-management practices for pesticide use are highly specific to crops and locations.
Looking for other ways to read this?
Following is a list of variables that affect and conditions that increase the likelihood of pesticides leaching into groundwater:. A number of universities and agencies in various locations for example, Hawaii, New York, Pennsylvania, Minnesota, and Florida are using geographic information systems to identify aquifers vulnerable to contamination by pesticides. The management practices that can be used to reduce pesticide pollution of surface water and groundwater are discussed below in greater detail.
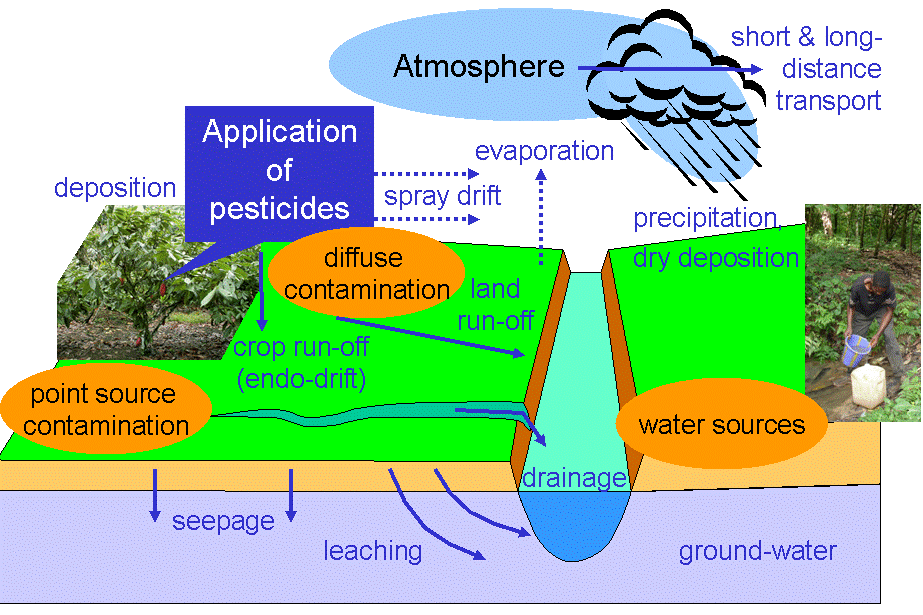
Figure presents a comprehensive scheme of the fates of pesticides applied in agroecosystems. Despite the vast knowledge base for the reactivity and transport of pesticides, a complete mass balance of the fate of any field-applied pesticide does not exist in the literature. Investigators have difficulty obtaining mass balances of the fates of pesticides for a number of reasons.
Pesticides include a broad class of agrichemicals with widely ranging properties and behaviors that defy generalizations.
There are technical difficulties and high costs associated with measuring over time the fraction of pesticides present in the various multimedia compartments and subcompartments in Figure Some processes, such as volatilization, sorption, photolysis, foliar washouts, and surface runoffs, occur over short time intervals for example, hours and days , whereas others occur over long time intervals for example, months and decades , such as hydrolysis, microbial degradation, and transport through the vadose region for cases in which the water table is many tens of meters below the land surface the vadose region is that part of the soil above the permanent groundwater level.
Recognizing this dilemma of acquiring an adequate mass balance, a concerted effort to obtain mass balances is being made through modeling see below. Some researchers have estimated that only 1 to 2 percent of insecticides applied to foliage is absorbed by the target pest. They base this estimate on a synthesis of conceptual mass balance. Figure , for example, is a mass balance for a typical aerial spray-foliar application of an insecticide. The hypothetical mass balance in Figure indicates problem areas where the efficacies of pesticide applications can be improved.
Even though a complete mass balance may not be available for a specific field case study, a few examples of the measured fates of pesticides from numerous literature sources would give some perspective. During the application stage of pesticide use, considerable losses may occur through spray drift and volatilization.
Spray drift constitutes about 3 to 5 percent of the loss under quiescent wind conditions, but it is typically much greater 40 to 60 percent for many insecticides. Loss from volatilization ranges from 3 to 25 percent, but it may be as great as 20 to 90 percent for methylparathion, for example, depending on weather conditions.
With regard to the efficacy of pesticide applications, losses to soil and peripheral nontarget foliage may be as high as 60 to 80 percent for most sprays Cheng, In contrast, pesticide losses from soil-incorporated application methods are much lower. Field measurements of pesticides applied by such practices reveal that the portion of pesticide volatilized is 2 to 12 percent for most pesticides but could be as high as 50 to 90 percent for volatile chemicals such as trifluralin.
Seasonal losses of pesticides in surface runoffs are typically in the range of less than 1 to 5 percent Wauchope, ; the lower losses are for foliar-applied organochlorines like toxaphene, and the higher losses are for wettable powders such as triazine. Pesticide loss through leaching into groundwater is another major component in the mass balance.
Factors contributing to the vulnerability of groundwater contamination were discussed above. The mass flux for leaching is sometimes taken at some prescribed soil depth, like the bottom of the root zone or the surface of the groundwater table. It should be noted that within the crop root zone and in the vadose region the pesticide is subject to numerous degradation and immobilization mechanisms. Based on a transport model that considered diffusive and mass flows as well as sorption and decay Tanji, a , the peak concentration is expected to be about 0.
That peak concentration of. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment. Beneath the Bottom Line: DBCP at the bottom of the vadose region was expected to be diluted to about 0. The cumulative loss of DBCP from the soil surface to the groundwater, therefore, was about These calculations, which involved 31 years of travel time, indicate that even a persistent chemical like DBCP is subject to huge sink losses, but because the maximum contaminant level set by EPA is so low 0.
Given the difficulty of obtaining mass balances on the fates of pesticides applied to croplands and the fact that minuscule losses to particular portions of the environment may be hazardous, a concerted effort must be made to increase the efficiency of pesticide use. Since everything must go somewhere, source control is the best approach. Computer simulation models are used as tools to evaluate more fully the fate and transport of pesticides in agricultural systems.
Spray pesticide models Cheng, based on diffusion or ballistics are available for the design and evaluation of spray application systems to minimize aerial drift and volatile losses as well as to elevate accurate targeting of the spray. Pesticide runoff models Cheng, from the small plot to the watershed-scales are being used to develop best-management practices. Considerable efforts were initially made toward determining the hydrologic processes that contribute to runoff and erosion. The reactivities of pesticides were then coupled to runoff models.
For the most part, these runoff models are more useful for evaluation of alternative management strategies and are less useful for predictive purposes. More recently, a concerted effort has been made to model pesticide leaching. Modeling of pesticide behavior and the leachabilities of pesticides. Conceptual screening models for pesticides typically consider solubility, sorption, persistence, volatility, and mobility.
- Heal Yourself From Any Disease and Other Articles!
- The Legendary Biographies of Tamerlane (Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization).
- Medicine and the Market: Equity V. Choice.
- New Pesticides and Soil Sensors.
- Product details.
- Navigation menu.
- Soldier of God (McGarvey).
Such models rank the behavior of the pesticide and its potential movement in soil. One example is that prepared by Rao and Hornsby see Table A more comprehensive approach is that of Jury and colleagues , in which chemicals are screened under idealized, standardized scenarios. However, screening models are not environmental fate prediction models and are inappropriate outside the idealized conditions that lead to their derivation.
Process-based simulation modeling for pesticide reactivity and transport has received a more intensive effort. These research-oriented models require extensive input data and have mainly been tested in laboratory soil columns and small-scale research plots.
Sources of Agricultural Pesticides
Jury and colleagues and Green and colleagues have pointed out some difficulties in predicting groundwater contamination by chemicals even with state-of-the-art simulation models. They point out that the convection-dispersion models appear to be unable to predict pesticide transport in the vadose zone. The reasons contributing to this dilemma include the spatial variability in the hydraulic properties usually encountered in field soils, the potential nonequilibrium sorption in the field, the depth dependency of biodegradation, and preferential flow through macropores.
Such considerations need to be incorporated into pesticide leaching models for improved model performances. Most recently, Pennell and colleagues compared the performances of five simulation models for simulating the behaviors of aldicarb and bromide from a given field study. Groundwater in artesian aquifers have enough pressure to flow all the way to the surface. The detection of pesticides in aquifers that are hundreds of feet deep has increased concern about the eventual fate of pesticides applied to croplands.
GLEAMS and MOUSE underestimated bromide and aldicarb dissipations, whereas the other models proved satisfactory in predicting both the depth of the solute's center of mass and the amount of pesticide degradation. None of the models, however, accurately predicted the pesticide concentrations measured throughout the soil profile. In addition to possible deficiencies in the model, the investigators pointed out the potentially large sampling error in the field because of spatial variability.
Mathematical models of surface runoff and leaching of pesticides have been constructed, tested, and used with varying degrees of success. The formulation of each model varies according to the objectives of the modeling exercises and the professional training and biases of the model developer.
The result has been a collection of approaches applicable to descriptions of surface runoff processes and a second body of efforts that have focused on leaching processes. Investigators have not often attempted to make comprehensive simultaneous descriptions, and when they have, the results have been complex, data-intensive models that cannot easily be used by anyone other than the developer Wagenet and Rao, A number of models simulate surface runoff and the resultant pesticide loading of surface waters Adams and Kurisu, ; Bruce et al.
In almost all cases, the models represent a compromise between the available data, which are often quite sparse and variable, and the need for a predictive tool that can be used across different soils, climates, and pesticides. Investigators have obtained mixed results with these models. To date there is apparently no increased predictive capability obtained by using models that are more mechanistic and data-intensive than using models that provide less of an understanding of the field-scale processes related to pesticide loss including surface hydrological processes. Soil leaching models of pesticide fates contain similar problems, although the basic physical, chemical, and biological processes in the soil are perhaps better-defined than surface hydrology processes.
Useful field-scale models exist in both mechanistic Carsel et al. Neither mechanistic nor empirical models have been widely tested under field conditions. The empirical versions are generally intended for qualitative educational purposes rather than quantitative regulatory purposes. A number of solute transport models that are intermediate between the mechanistic and nonmechanistic extremes have been proposed reviewed by Addiscott and Wagenet, , but they have yet to be applied to pesticide leaching by water.
The spatial variability of soil processes also has generated interest in stochastic or probabilistic approaches to describing chemical leaching in soil Jury et al. These approaches may prove to be the most useful because they show promise as descriptors of spatially variable processes, yet they are neither as mathematically cumbersome nor as computationally demanding as current mechanistic models Wagenet and Rao, Stochastic or probabilistic approaches can also account for the stochastic nature of precipitation and its effect on leaching or runoff Hornsby, Although not all of these groundwater models would be suitable for simulating pesticide transport, some should be directly applicable.
These new modeling efforts, however, are not typically incorporated into pesticide leaching models; hence, incorporation will require considerable effort on the part of modelers researching the transformations and transport of pesticides in agricultural systems. The management practices that can be used to reduce environmental pollution from pesticide use in agroecosystems can be broadly categorized into. Source control or reducing the amounts of pesticides used should be the first line of action.
Pesticides should be used only when and where they are necessary and only in amounts adequate to control the target pest. If a potential pesticide user can choose among a number of available pesticides, the user should select those that will be least harmful to the environment. For many conditions, the characteristics of a selected pesticide should include low water solubility, high sorptive capacity, low vapor pressure, higher potential for chemical and microbial degradation, and shorter overall half-life in the field.
Although pesticides are formulated mainly for ease of application, the natures of the formulations do have some impacts on potential losses to the environment. For instance, use of pesticides in the granular, pelleted, or emulsified form results in less drift and volatile losses during application. Pesticides in the form of dusts, wettable powders, or fine liquid sprays are more subject to drift losses.
Pesticides applied as liquid mixtures or concentrated solutions have greater potential for loss through volatilization. Those pesticides in wettable powders are more susceptible to runoff losses. Rotating crops provides productivity benefits by improving soil nutrient levels and breaking crop pest cycles. Farmers may also choose to rotate crops in order to reduce their production risk through diversification or to manage scarce resources, such as labor, during planting and harvesting timing.
This strategy reduces the pesticide costs by naturally breaking the cycle of weeds, insects and diseases. Also, grass and legumes in a rotation protect water quality by preventing excess nutrients or chemicals from entering water supplies. Farmers in Shandong China have been using innovative methods to control bollworm infestation in cotton when this insect became resistant to most pesticides. Among the control measures implemented were:. These and some additional biological control tools have proved to be effective in controlling insect populations and insect resistance, protecting surroundings and lowering costs.
Many in the agricultural community have adopted the sense of urgency and direction pointed to by the sustainable agriculture concept. Sustainability has become an integral component of many government, commercial, and non-profit agriculture research efforts, and it is beginning to be woven into agricultural policy. Increasing numbers of farmers and ranchers have embarked on their own paths to sustainability, incorporating integrated and innovative approaches into their own enterprises. Fisher, Editor is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. Skip to content Increase Font Size.
Biological Control Figure 1. Intercropping Promotes Plant Interactions. Among the control measures implemented were: The use of pest resistant cultivars and interplanting of cotton with wheat or maize. Aiming to improve work efficiency in such areas as tillage in agriculture, earth-moving in civil engineering, and tunnel-making in sea-bed operations, this work offers an introduction to Finite Element Method FEM analysis of soil-machine systems.
It explains the advantage of FEM's numerical…. Frankenberger , Richard A. Presents basic and the most recent applied research developments in selenium remediation-emphasizing field investigations as well as covering topics from analytical methods and modeling to regulatory…. This work features scientific, technical and practical information on mineral, organic and synthetic conditioners, as well as their beneficial effects on the soil's physical properties that promote optimal plant growth, maximize soil fertility, and enhance biomediation processes.
This work integrates basic biotechnological methodologies with up-to-date agricultural practices, offering solutions to specific agricultural needs and problems from plant and crop yield to animal husbandry. It presents and evaluates the limitations of classical methodologies and the potential of…. The book discusses methodologies from linear programming and neutral networks, to expert or decision support systems, as well as featuring models, such as SOYGRO….
Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment Handbook of Photosynthesis 3rd Edition Edited by Mohammad Pessarakli Since the publication of the previous editions of the Handbook of Photosynthesis, many new ideas on photosynthesis have emerged in the past decade that have drawn the attention of experts and researchers on the subject as well as interest from individuals in other disciplines.
Tan The field of humic matter research has undergone drastic changes in concepts and principles since the first edition of Humic Matter in Soil and the Environment: Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology 3rd Edition Edited by Mohammad Pessarakli Continuous discoveries in plant and crop physiology have resulted in an abundance of new information since the publication of the second edition of the Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology, necessitating a new edition to cover the latest advances in the field. Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress 3rd Edition Edited by Mohammad Pessarakli The dynamic and expanding knowledge of environmental stresses and their effects on plants and crops have resulted in the compilation of a large volume of information in the last ten years since the publication of the second edition of the Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress.
Tan Learn the secrets of soil chemistry and its role in agriculture and the environment. Daniels , Mohammad Reza Ehsani Precision farming, site infrastructure assessment, hydrologic monitoring, and environmental investigations — these are just a few current and potential uses of near-surface geophysical methods in agriculture. Tan Highlighting the vast differences in tropical climate, from hot and humid to cool and arctic, Soils in the Humid Tropics and Monsoon Region of Indonesia explores the climate, soil zones, and altitudinal variation in soil formation.
Handbook of Turfgrass Management and Physiology Edited by Mohammad Pessarakli A multibillion dollar industry that has tripled in the last ten years, turfgrass management plays an important role in landscaping, golf courses, and other sports surfaces. Proper management and cultural practices are crucial for the performance of these versatile grasses, creating a demand among… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Vidhyasekaran Dramatic progress in molecular biology and genetic engineering has recently produced an unparalleled wealth of information on the mechanisms of plant and pathogen interactions at the cellular and molecular levels.
Functional Plant Ecology 2nd Edition Edited by Francisco Pugnaire , Fernando Valladares Following in the footsteps of the successful first edition, Functional Plant Ecology, Second Edition remains the most authoritative resource in this multidisciplinary field. The Rhizosphere Biochemistry and Organic Substances at the Soil-Plant Interface, Second Edition Edited by Roberto Pinton , Zeno Varanini , Paolo Nannipieri In the rhizosphere, exudates from plants and microorganisms as well as stable soil organic matter influence processes that can control plant growth, microbial infections, and nutrient uptake.
As the chemistry and biochemistry of these substances becomes more and more clear, their study promises to… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Jansson , Paola Nannipieri In the ten years since the publication of Modern Soil Microbiology, the study of soil microbiology has significantly changed, both in the understanding of the diversity and function of soil microbial communities and in research methods.
Organic Production and Use of Alternative Crops By Franc Bavec , Martina Bavec Merging coverage of two increasingly popular and quickly growing food trends, Organic Production and Use of Alternative Crops provides an overview of the basic principles of organic agriculture and highlights its multifunctionality with special emphasis on the conservation of rare crops and their… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Biodiversity In Agricultural Production Systems Edited by Gero Benckiser , Sylvia Schnell While modern science has always recognized the central role that biodiversity plays in the ecological processes that maintain the Earth's equilibrium, our increasing knowledge of nature has deepened our appreciation of this principle.
It analyzes many recently developed measurement tools, and explains computer-related and pedometric techniques that are invaluable… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Water Flow In Soils 2nd Edition By Tsuyoshi Miyazaki The new edition of a bestseller, Water Flow in Soils bridges the fields of soil physics-where descriptions of water flow tend to be microscopic- and hydrology - where they tend to be macroscopic. Unlike other physics laden texts, this work conveys the fundamental concepts of water flow in soils… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment.
Hansen In order to feed their burgeoning populations, developing nations will need to double cereal production by the year This increase will have to come from existing land, as little potential exists for bringing new land under cultivation -- a daunting prospect when one realizes that increased… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Tan As with the highly popular original, this new edition of Soil Sampling, Preparation, and Analysis provides students with an exceptionally clear description of the sampling and analysis methods most commonly used in modern soil laboratories around the world.
Wilhite Today the world is facing a greater water crisis than ever.
Agricultural Pesticides and Human Health
Elstner In order to keep track of all the compounds and pathogens affecting plant metabolism and development, you would need to spend all your waking hours combing periodicals and the Internet in dozens of languages, as new toxins via pollutants and migratory or mutant pathogens are being discovered… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Shukla Principles of Soil Physics examines the impact of the physical, mechanical, and hydrological properties and processes of soil on agricultural production, the environment, and sustainable use of natural resources.
Hobbs , Norman Uphoff , Rattan Lal Addressing a topic of major importance to the maintenance of world food supplies, this reference identifies knowledge gaps, defines priorities, and formulates recommendations for the improvement of the rice-wheat farming system. With a history of around four billion years, water has been around since the early days of… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. David Shoup Running a productive agriculture system has always been about having the right tools and the know-how to pursue optimization and efficiency.
Meeting this demand by increasing production through increased land use is not very likely; and while better crop management may make a marginal difference, most agriculture… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Cresser Evaluating traditional and recent analytical methods according to speed, sensitivity, and cost-efficiency, this reference supports specialists in the selection of effective analytical techniques and equipment for the study of soils, soil contaminants, and environmental samples.
Scholtz III Highlighting effective, analytical functions that have been found useful for the comparison of alternative management techniques to maximize water and nutrient resources, this reference describes the application of viable mathematical models in data analysis to increase crop growth and yields.
Wheeler Discussing the range of effects of pesticides on food and human safety, water quality, wildlife, and pest management, this book explores the agricultural, economic, and regulatory factors that affect pesticide use. Dick The need to understand the biological processes that are important for essential aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem function has prompted much research into the field of ecological enzymology.
This book presents the two broad areas of application in a compilation of reviews by 21 international… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Frankenberger, Jr With contributions from world-renowned experts in the field, this book explores developments in the transport kinetics, seasonal cycling, accumulation, geochemistry, transformation, and toxicology of arsenic. Narayanasamy This work provides information on the detection, identification, and differentiation of all microbial plant pathogens - presenting modern protocols for rapid diagnosis of diseases based on biological, physical, chemical and molecular properties.
Prasad A summary of data on heavy metal accumulation, biomonitoring, toxicity and tolerance, metal contamination and pollution in the environment, and the importance of biodiversity for environmental monitoring and cleanup of metal-contaminated and polluted ecosystems. Bovey A presentation of strategies for managing woody plants and using research data to select the most appropriate control methods. Microbial Pest Control By Sushil Khetan A complete overview of the technologies and products for microbial-based pest control.
It documents the use of genetically altered Bt and transgenic crops, microbial formulations, and synergistic interactions of microbials with synthetic chemicals, as well as the management of Bt foliar… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Smith "Reviews a wide range of methods for soil physical analysis.
Soil Biochemistry, Volume 10 Edited by Guenther Stotzky An exploration of the most complex microbial ecosystems with incisive reviews of developments in soil science. Microbial Endophytes Edited by Charles W. Bacon , James White Examining intercellular infections in certain plant species that lead to a symbiotic relationship between the host and its endophytic microbes, this volume demonstrates the ability of many types of endosymbionts, acting as a unit with hosts to better survive, compete and reproduce.
Ruberson "Provides a detailed summary of pest management principles and techniques, outlining a broad selection of critical issues regarding current practice and future technology in this area. From Phytohormones to Genome Reorganization By Lerner Emphasizing the unpredictable nature of plant behaviour under stress and in relation to complex interactions of biological pathways, this work covers the versatility of plants in adapting to environmental change.
Singh Covers the basic knowledge of the regulation of biosynthesis of various amino acids in plants and the application of this knowledge to the discovery of novel inhibitors of amino acid biosynthesis and for enhancing the nutritional value of plant products. Shinha , Deepak Bhatnagar Describes a range of mycotoxins occurring as contaminants in agricultural crops and animal products, and details the implementation of food safety regulations via governmental and international agencies. Soil-Machine Interactions A Finite Element Perspective By Shen Aiming to improve work efficiency in such areas as tillage in agriculture, earth-moving in civil engineering, and tunnel-making in sea-bed operations, this work offers an introduction to Finite Element Method FEM analysis of soil-machine systems.
Engberg "Written as a complement to the definitive work selenium in the Environment Marcel Dekker, Inc.
Presents basic and the most recent applied research developments in selenium remediation-emphasizing field investigations as well as covering topics from analytical methods and modeling to regulatory… Hardback — CRC Press Books in Soils, Plants, and the Environment. Substances That Enhance the Physical Properties of Soil By Wallace This work features scientific, technical and practical information on mineral, organic and synthetic conditioners, as well as their beneficial effects on the soil's physical properties that promote optimal plant growth, maximize soil fertility, and enhance biomediation processes.