Free download.
Book file PDF easily for everyone and every device.
You can download and read online Pancreatic Pseudocysts file PDF Book only if you are registered here.
And also you can download or read online all Book PDF file that related with Pancreatic Pseudocysts book.
Happy reading Pancreatic Pseudocysts Bookeveryone.
Download file Free Book PDF Pancreatic Pseudocysts at Complete PDF Library.
This Book have some digital formats such us :paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, fb2 and another formats.
Here is The CompletePDF Book Library.
It's free to register here to get Book file PDF Pancreatic Pseudocysts Pocket Guide.
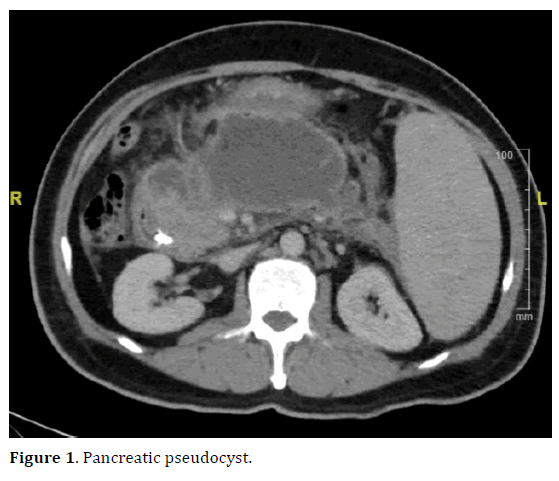
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the.
Table of contents
- On this page:
- Pancreatic Pseudocysts in Patients with Cholithiasis
- Pancreatic Pseudocysts in Patients with Cholithiasis - SAGES Abstract Archives
Such procedures should only be undertaken by experienced endoscopic interventionalists in high volume centers that have back up by skilled hepatobiliopancreatic surgeons and interventional radiologists. Use of carbon dioxide insufflation is mandatory to avoid air embolism.
An echoendoscope with an antegrade view of degree and 3. The straight instrument channel allows better instrument control due to reduced resistance.
On this page:
Compared to conventional linear echoscopes the antegrade type has curved linear array with a much shorter rigid portion at the tip and a capability to angulate the tip up to degree which improves manoeuvrability and e. An auxillary water channel flushes away blood and turbid cyst contents for clear endoscopic views.
First studies including a randomized controlled multicenter trial have shown promising results compared to conventional longitudinal echoendoscopes[ 18 - 20 ]. Usually, metal stents are not required to drain pseudocysts containing clear fluids but for infected cysts and walled-off necrosis a long term securing of a large diameter cyst opening by a metal stent can be helpful to allow drainage of larger particles and repeated direct endoscopic debridement Figure 1.
Large flanges should prevent dislocation of the stent, particularly feared is the migration of the stent into the necrotic cavity. The stents are covered to avoid leakage between cyst and stomach wall, it also prevents ingrowth and enables easy removal at a later timepoint. The self-extendable metal stents designed for drainage of pancreatic fluid collections and necrosis open to an internal diameter of more than 1 cm lumen to allow direct and repeated endoscopic access for endoscopic necrosectomy and extraction of necrotic tissue Figure 2.
The covered stent produced by Hananro has extraflanges at the gastric end to stop migration into the cyst Table 3. This can be adventageous in pancreatic fluid collections with indeterminate wall adherence. Recent studies demonstrate a lower occlusion rate and the need for only one stent insertion due to the large diameter, the option for endoscopic access to the cavity as clear advantages of SEMS compared to conventional stents[ 23 - 26 ]. The migration risk remains. Some interventionalists place a double pigtail stent through the metal stent to prevent stent dislocation. The cystostome already combines the cyst puncture with an inner needle knife catheter followed by the diathermy by a metal ring at the tip of the outer sheet[ 27 ].
Exchange over a wire for stenting is still necessary. However, a new development also now comes with a preloaded straight stent which can be placed directly after diathermy. The Giovannini stent device[ 28 ] is an all-in-one stent introduction system combining a 0. The needle-wire is introduced under EUS-guidance into the fluid collection using cutting current. After removing the internal rigid part, the wire can be curled in the cystic cavity to stabilize the position.
The guiding and dilatation catheter follows over the wire and finally the straight plastic stent can be transmurally positioned Giovannini Needle Wire Oasis; Cook endoscopy, Winston-Salem, NC, United States. This one-step EUS-guided technique for transmural cyst access has proven safe and effective for the management of pancreatic pseudocysts and abscesses[ 29 ]. The side blade enlarges the ostium to 3. The device has also additional channels for guide wires and contrast injection[ 30 ].
Avoiding device exchanges, this accessory allows access, guidewire insertion, tract enlargement and dilatation.
The recent technical developments have provided us with easier deployable stent systems for the EUS-guided management of pancreatic fluid collections. The SEMS appear safer and more effective in hitherto existing case series and studies. Large-sized, randomised comparative studies are required for further evaluation and this will lead to continued improvement of the techniques.
Advanced Search. This Article. Citation of this article. Braden B, Dietrich CF. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts and walled-off necrosis: New technical developments. Corresponding Author of This Article. Publishing Process of This Article.
Research Domain of This Article. Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Article-Type of This Article. Open-Access Policy of This Article. This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. Number of Hits and Downloads for This Article.
Total Article Views All Articles published online. Times Cited of This Article. Journal Information of This Article.
- Indestructible Hulk #16?
- Surgery (21st Century Skills Innovation Library: Innovation in Medicine).
- К жизни (K zhizni): Russian edition.
- Pancreatic pseudocyst | UF Health, University of Florida Health!
- Pancreatic pseudocysts?
- Don't have a user account?.
- Alcatraz Escape Attempts.
All rights reserved. World J Gastroenterol. Christoph F Dietrich, Med. Klinik 2, Caritas Hospital, Uhlandstr. Key Words: Pancreatic pseudocyst , Walled-off necrosis , Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage , Self-expanding metal stent , Acute pancreatitis. Ultrasound processor Linear array echoscope with 3. New self-expandable metal stents. A: Gastric end of the covered transmural stent; B: Endoscopic view within the stent showing blocking necrotic material; C: Endoscopic view of the necrotic cavity after passage of the endoscope through the metal stent two weeks after flushing via a nasocystic tube.
Tech 30 or 40 10 or 12 25 Classification of acute pancreatitis revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Combined endoscopic and percutaneous drainage of organized pancreatic necrosis. Gastrointest Endosc. Dual-modality drainage of infected and symptomatic walled-off pancreatic necrosis: long-term clinical outcomes. Severe acute pancreatitis: nonsurgical treatment of infected necroses.
Pancreatic Pseudocysts in Patients with Cholithiasis
Outcome of severe acute pancreatitis: is there a role for conservative management of infected pancreatic necrosis? Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. Primary conservative treatment results in mortality comparable to surgery in patients with infected pancreatic necrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided versus conventional transmural drainage for pancreatic pseudocysts: a prospective randomized trial.
Ultraschall Med. Giovannini M.
Pancreatic Pseudocysts in Patients with Cholithiasis - SAGES Abstract Archives
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic drainage. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. World J Gastrointest Endosc. Multiple transluminal gateway technique for EUS-guided drainage of symptomatic walled-off pancreatic necrosis.